명령프롬토프 관리자권한으로 시행
wsl --instlall 실행하고 아래 명령어 실행해줘야 인식됨
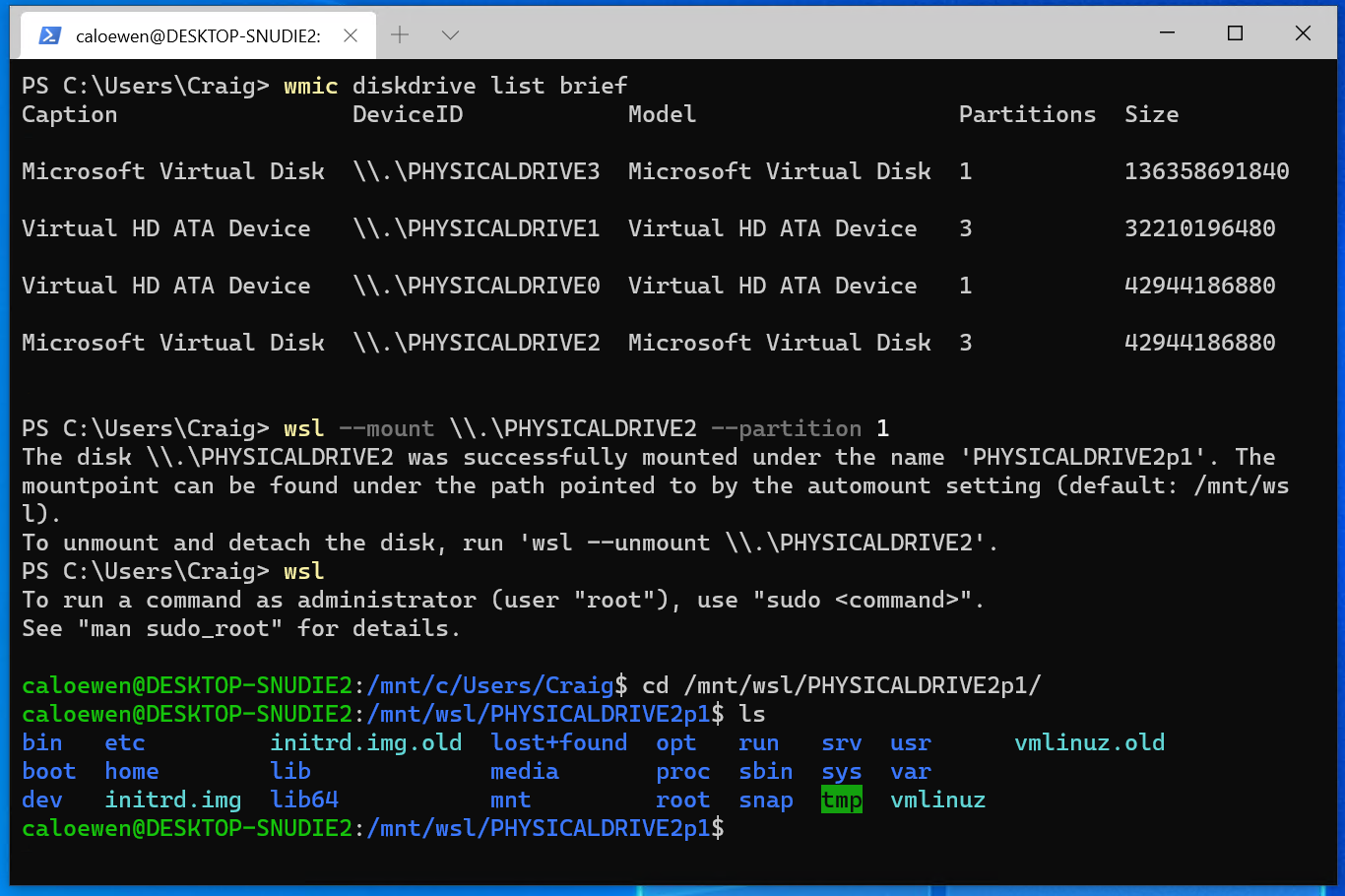
디스크 드라이브 리스트보기
wmic diskdrive list brief
Starting with Windows Insiders preview build 20211, WSL 2 will be offering a new feature: wsl --mount. This new parameter allows a physical disk to be attached and mounted inside WSL 2, which enables you to access filesystems that aren’t natively supported by Windows (such as ext4).
So, if you’re dual booting with Windows & Linux using different disks, you can now access your Linux files from Windows!
Getting started
To mount a disk, open a PowerShell window with administrator privileges and run:
wsl --mount <DiskPath>To list the available disks in Windows, run:
wmic diskdrive list briefTo unmount and detach the disk from WSL 2, run
wsl --unmount <Diskpath>The disks paths are available under the ‘DeviceID’ columns. Usually under the \\.\\\.\PHYSICALDRIVE* format. Below is an example of mounting a specific partition of a given hard disk into WSL and browsing its files.
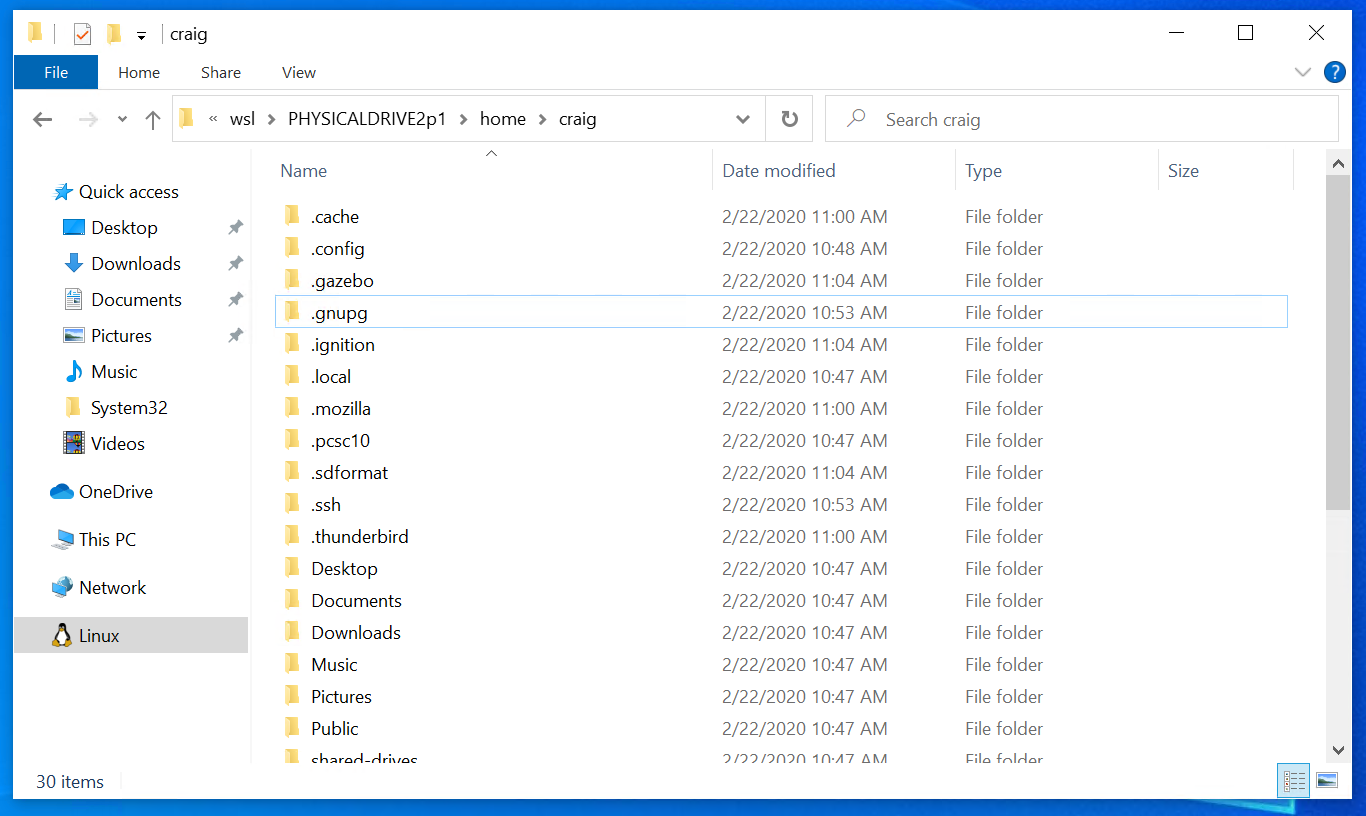
Accessing these files with File Explorer
Once mounted, it’s also possible to access these disks through the Windows explorer by navigating to \wsl$ and then to the mount folder.
Limitations
By default, wsl --mount attempts to mount the disk as ext4. To specify a filesystem, or for more advanced scenarios, check out Mount a disk in WSL 2.
Also please note that this feature comes with the limitation that only physical disks can be attached to WSL 2. At this time, it’s not possible to attach a single partition. More details on the limitations here.